|
 Keeping track of time is ever-present in our normal working lives, all the more so during These Difficult Times™, and the subject has featured in many ToW’s passim. Keeping track of time is ever-present in our normal working lives, all the more so during These Difficult Times™, and the subject has featured in many ToW’s passim.
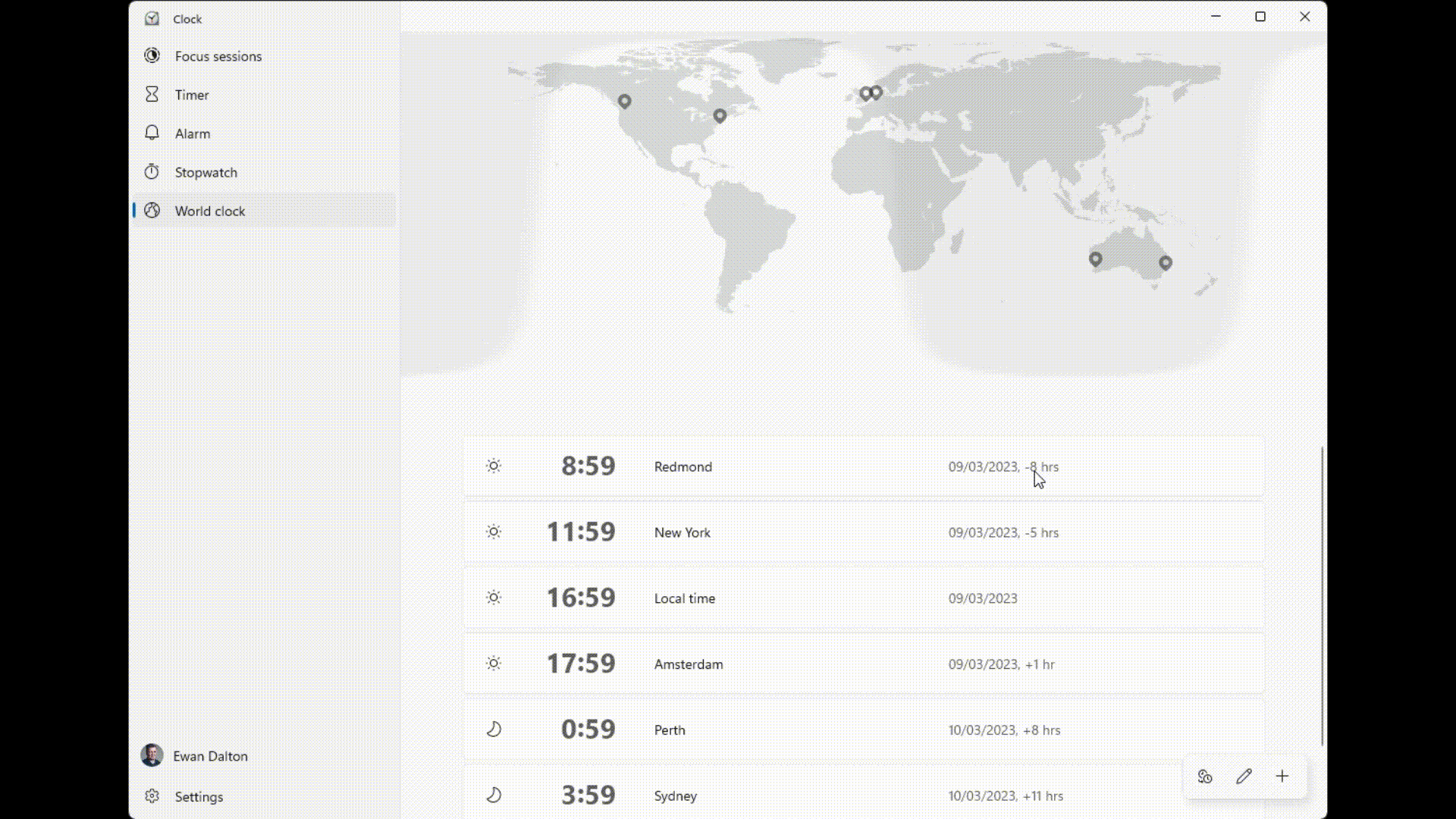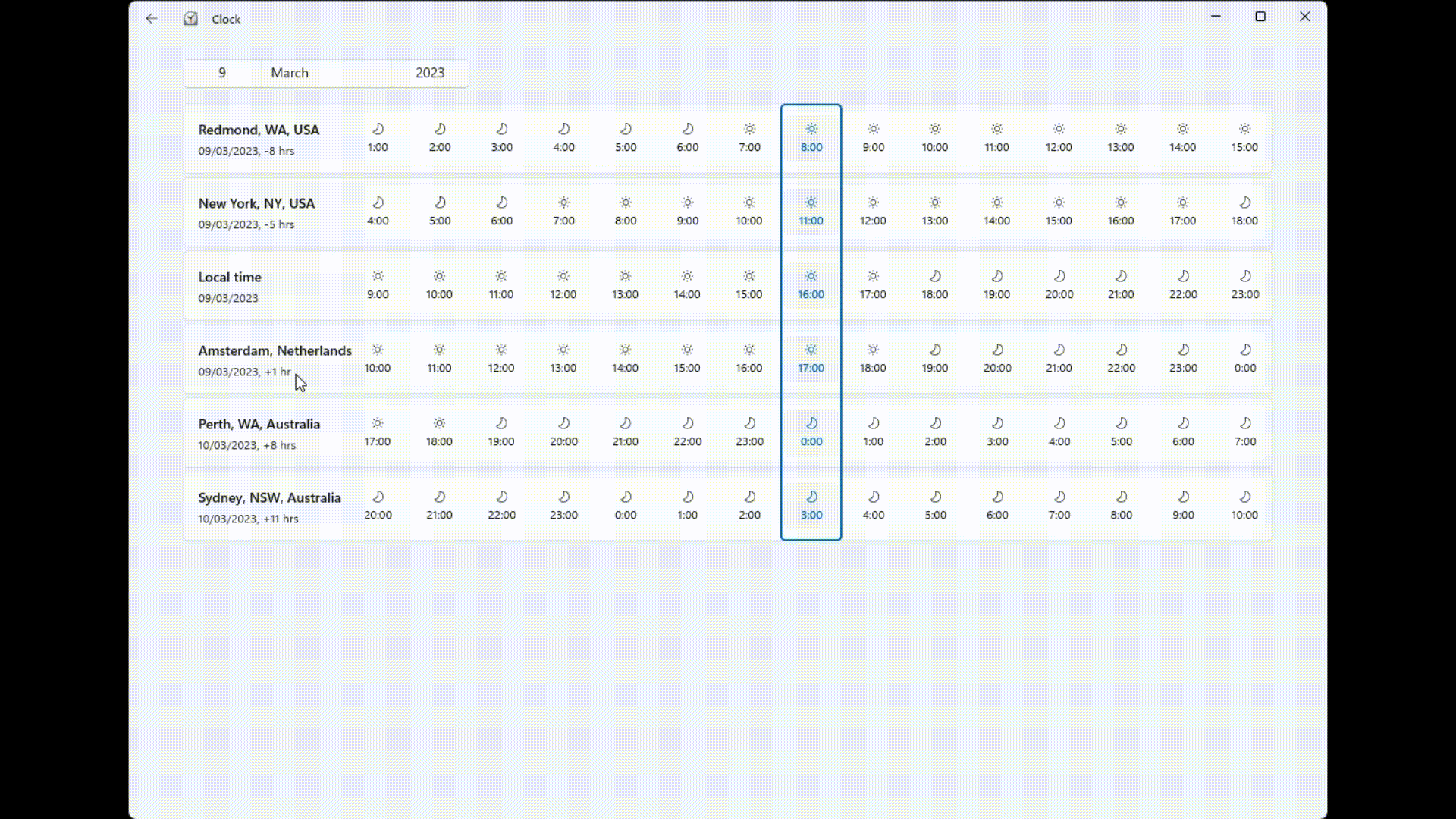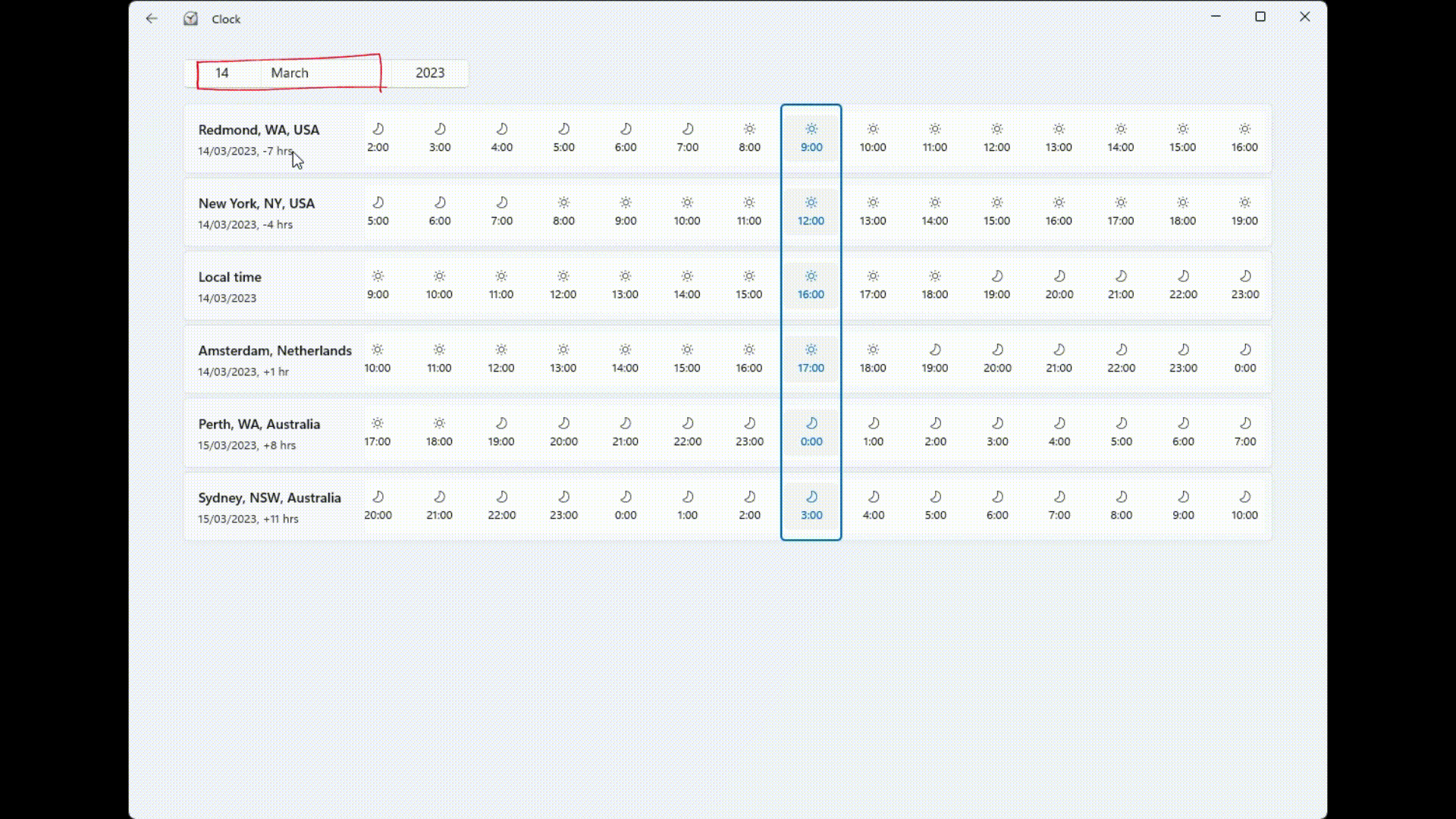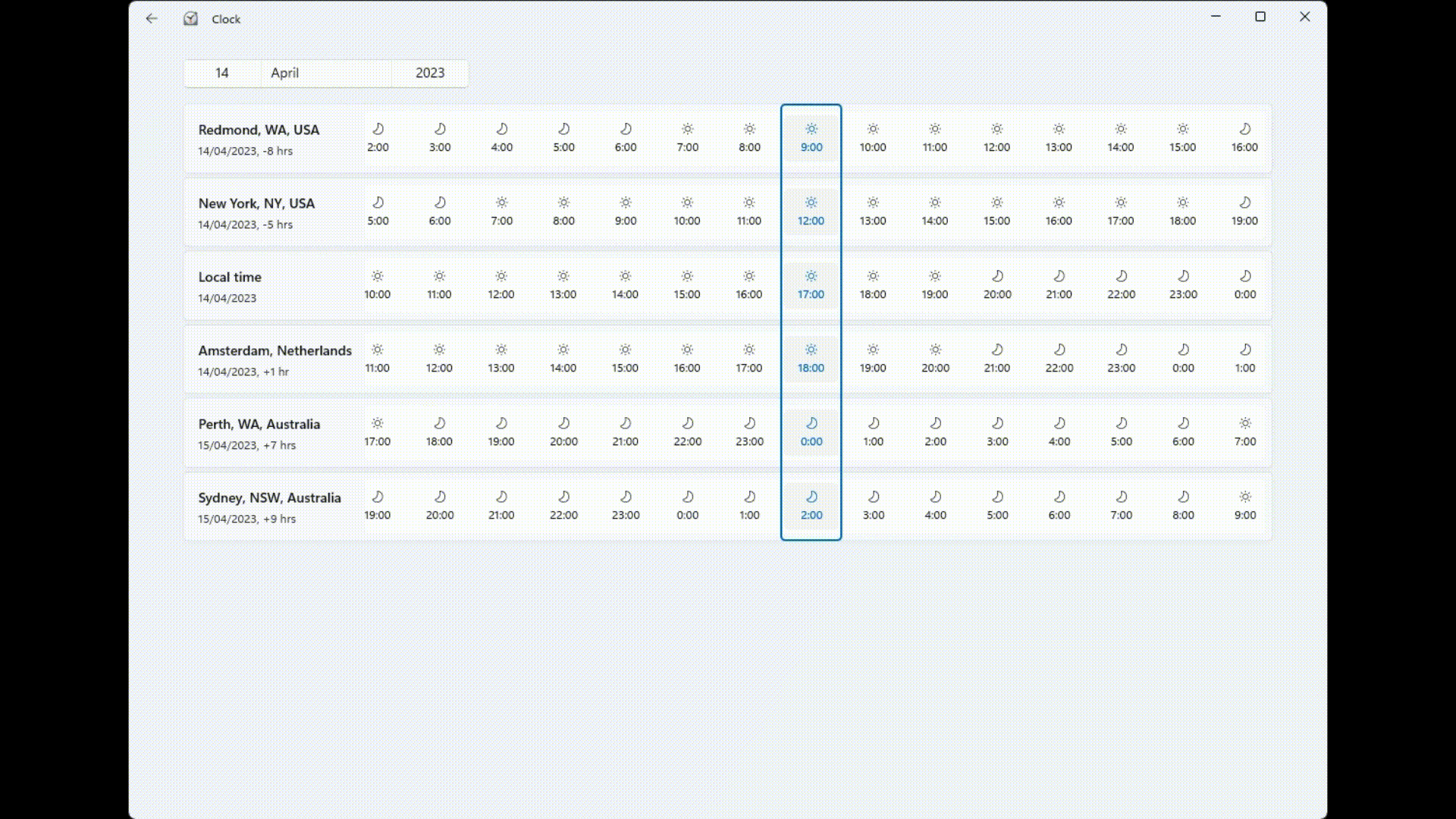
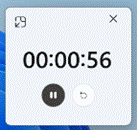
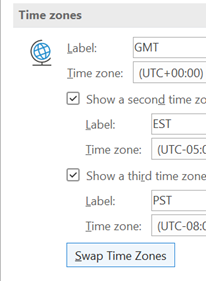
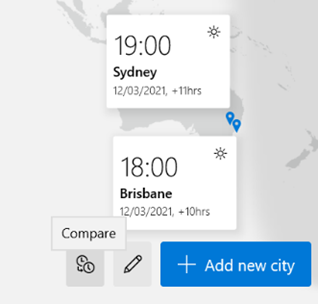
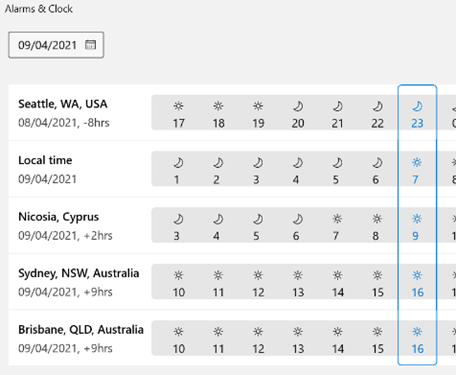
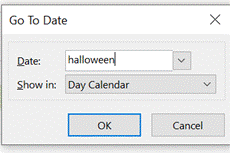
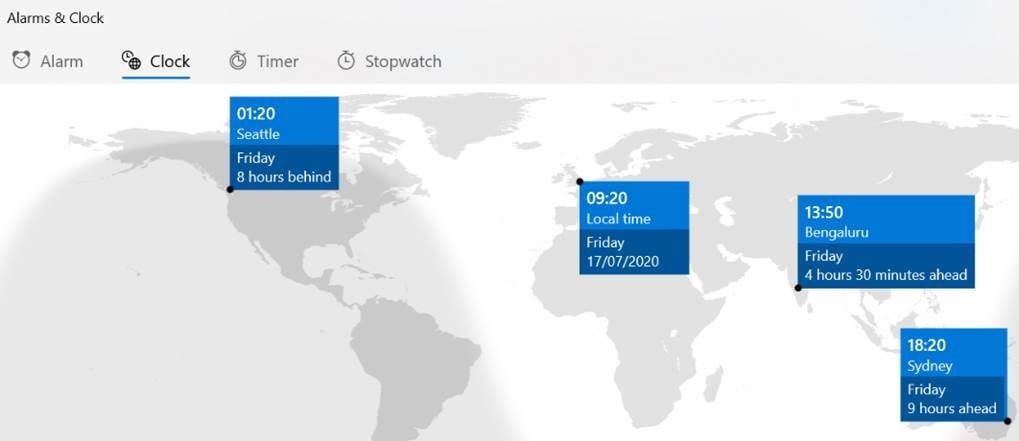
There’s a great little app built-in to Windows 10 called Alarms & Clock, which lets you set alarms on your PC, show a world map with multiple locations / time zones displayed, and also provides a neat countdown or count-up timer.
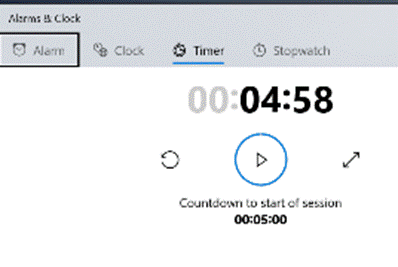 Using the timer function can be pretty handy if you’re speaking as part of an online meeting, and need to keep a check on how long you have left to go. Using the timer function can be pretty handy if you’re speaking as part of an online meeting, and need to keep a check on how long you have left to go.
You can create multiple separately-controlled timers with different durations & names; so you could have an overall meeting countdown timer, and then a separate one for each participant, if you were acting as the time cop to keep everyone else in line.
The Stopwatch is simply a fast-running counter of elapsed time, and by using the  icon on either Timer or Stopwatch screens, you can easily fill the display to help focus on the elapsed or remaining time. Handy if you’re in a physical meeting (remember them?) and are able to display a laptop screen showing the time for everyone. icon on either Timer or Stopwatch screens, you can easily fill the display to help focus on the elapsed or remaining time. Handy if you’re in a physical meeting (remember them?) and are able to display a laptop screen showing the time for everyone.
Those of us who still wear physical, mechanical wristwatches may be passingly familiar with a few features that have existed for decades to achieve the same kind of function, albeit more for individual rather than shared use.
 Diver bezel Diver bezel
So called “diver” watches were popularised in the 1960s and 70s, as tough, waterproof and utilitarian. The most striking feature of any dive watch is generally the rotating numbered bezel which goes around the outside.
The simple idea was that when you entered the water (knowing you might have 20 minutes of air), you would turn the bezel so the arrow / zero marker was set to where the minute hand was at that point – meaning a later glance at the watch will tell you how many minutes have passed since.
Lots of other non-dive watches also have rotating bezels or indicators, and can be useful for things other than scuba – when the activity above started at 5 minutes to 10, the bezel was set, and it’s easy to see in a trice that was 11 or 12 minutes ago. Not sub-second accurate, but it’s a simple way to mark the passing of time.
 Tachymetre /Tachymeter Tachymetre /Tachymeter
Many chronograph watches – which combine the function of a stopwatch and a regular timepiece – have a Tachymetre scale around the outside, yet most people these days will have no clue what it’s for. The basic function of the watch is that pusher buttons on the side will start and stop the movement of the chronograph hand which ticks round to indicate elapsed time.
The deal with the TACHY scale is that if you know a distance – the length of a straight on a motor-racing track, for example – and you time something going over that distance, then you can quickly calculate its speed across the ground.
In practice this is easier said than done, since the TACHY scale reads how many of the <distance> would be covered in an hour at this speed. If the measured distance was exactly 1km or 1mile then it’s an easy calculation – if it took 12 seconds to cover 1km, that would equate to 5km per minute or 300km/h. If the measured distance was a fraction – let’s say the length of the 12-second straight was 150m – then the calculation would be 300 x 150m per hour, or 45km/h. By the time you’ve done that in your head, the subject will be half a lap further on…
 Another variant on the theme would be if you know the speed – e.g. you’re in a plane with inflight map display, or passenger in a car on cruise control on the motorway – then you could use the Tachymeter to calculate distance travelled. Another variant on the theme would be if you know the speed – e.g. you’re in a plane with inflight map display, or passenger in a car on cruise control on the motorway – then you could use the Tachymeter to calculate distance travelled.
If you were cruising at 120km/h, and started the timer, then stopped it when it reached 120 on the scale… (after 30 seconds) – then you know you will have travelled 1km in that time.
Yes, there probably are hundreds of times a month when you need to know exactly this.
Pulsations
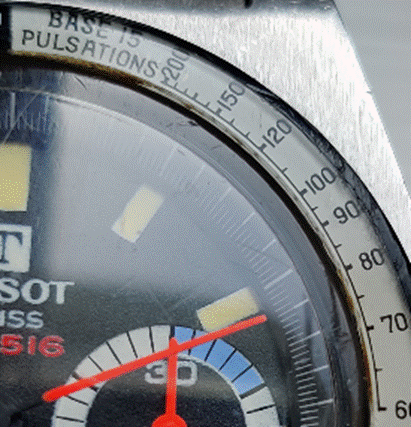 Slightly more useful to the average person, some chronographs have a Pulsations bezel rather than a Tachymeter scale, or maybe even have both (since the Tachymeter would typically be used for more than 15 seconds, it’s possible to have one quarter of the bezel represent pulsations and the rest of it be a Tachy). Slightly more useful to the average person, some chronographs have a Pulsations bezel rather than a Tachymeter scale, or maybe even have both (since the Tachymeter would typically be used for more than 15 seconds, it’s possible to have one quarter of the bezel represent pulsations and the rest of it be a Tachy).
Watches with Pulsations bezels are sometimes nicknamed “Doctors’ watches” as the utility is to help count a patient’s pulse – the method being you start the chronograph, count 15 pulses and the corresponding number on the bezel would tell you what the pulse/minute rate is.
Smart watches, eh, who needs them when you have space-age timing technology like this?
|
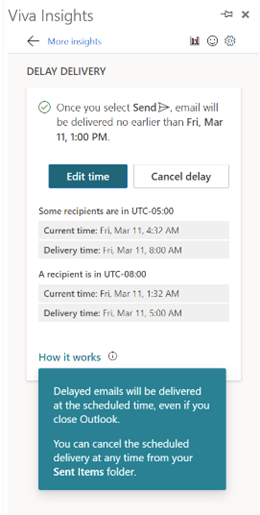
 noon SEA and 8pm LON, but now at a refreshing 5am SYD.
noon SEA and 8pm LON, but now at a refreshing 5am SYD.