|
OneNote has featured plenty in ToW previously, including a mention in the recent Journaling tip, with a nod in SteveSi’s ongoing historical missive which described members of the development team unhappy with the change of name from its code-name “Scribbler”, referring to the new “OneNote” app as “Onay-No-Tay”. A few years ago, OneNote was dropped from the Office suite and was due to be replaced by the new “modern” version in the Windows (now Microsoft …) Store. For a while at least, that shiny new one got all the innovation, even if its brand-new architecture meant it missed a lot of the old app’s functionality. In a somewhat surprising but welcome turn-around, old OneNote was reprieved, and both apps are going to converge at some later point – ie the desktop one will pick up features that only exist in the Store app, and eventually that version will cease to be.
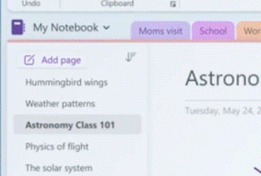
There’s a more prominent “Add Page” button More is to come, including improved sharing capabilities and a neat dictation functionality that would allow you to record a spoken explanation for something while using Ink to highlight or illustrate; when another user plays back your monologue, the ink will be synchronised too. For more info on what’s coming, see here.
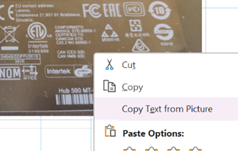
Copying screen-grabs when someone is doing a demo in a browser, so you can get the long and complex URL for the thing they’re showing is a particularly useful way of using this feature. |
Month: May 2022
631 – Why does nobody share calendars?
|
Even in 1990, NOSS allowed any user to browse a hierarchical directory (showing contact info, job titles, manager/reporting relationships etc), email or instant message anyone, and look at their calendar to see what they When Microsoft Exchange first came out, email was handled with the Exchange client and calendaring was from Schedule+, which had been updated to support Exchange (and lives on in some backward Microsoft lingo, where people who start every sentence with “So,” ask you to send them an S+, meaning, invite them to a meeting). Outlook came along in 1996 and became the preferred and unified way to do email, calendars, address books etc.
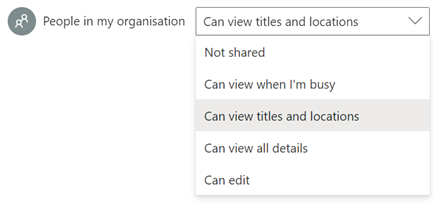
With M365 in general, newly-created mailboxes have no calendar sharing set up, and the action is on the user to choose how to let co-workers see their info. Be a nice person, and check to make sure your colleagues can view your calendar. Ideally, share so that others will see the title and location of any appointment; useful when someone is trying to arrange a meeting, as within the schedule view they can figure out if you are likely to be able to make the proposed meeting time – if your diary is full of blocks marked busy or tentative, they’ll have no idea if you really are in a meeting or have just marked time to do something that you might be happy to move. Or had a colleague’s FYI notice of being on holiday obliterate the view of your calendar. In the early days of Exchange/Outlook, if you had read access to someone’s calendar, you could open up appointments, see who else was attending a meeting, download any attachments and so on, unless the appointment was marked “Private” – though it’s somewhat possible to open Private appointments programmatically if you know what you are doing.
If you choose titles & locations, viewers can’t open your appointments to peer inside, so can’t see who else is attending or what the body of the meeting says, but they can at least see if you’re likely to need travel time between meetings. See here for more info on calendar sharing & delegate access. |
630 – slimming your PPT
|
Estimates of the energy cost to transmit and store data vary wildly, but if 1 GB cost 1 kWh power and the average CO2 output for generation was ~500g/kWh, then even shaving 10MB off a file can make a material difference if it’s going to be heavily used†. There are a few tricks you can follow to make your PPTs less massive – like compressing the images within, meaning that an embedded picture which was originally sized to print on a poster could be re-sized to fit on a screen.
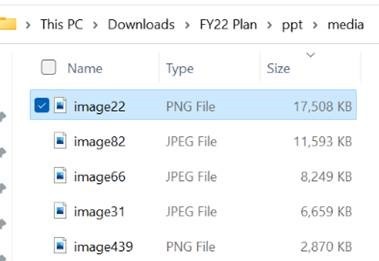
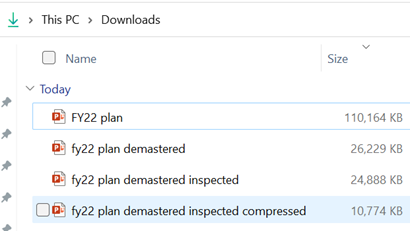
A somewhat cavalier way of looking for large things you can torch, is to make a copy of your PPTX file and then rename it so you can look within. The OfficeXML file formats (prevalent in Office 2007 and onwards) use the same compression as ZIP files, so if you rename your file as such, you’ll be able to open it in Windows Explorer or other ZIP handling utilities, to see its innards. Opening the file shows you a folder structure, and if you navigate into ppt \ media then sort by Size, you’ll quickly see what’s making your file so big.
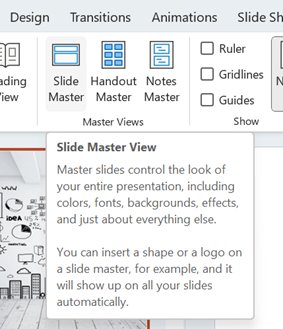
Go into View menu and look under Slide Master, which will open a whole new tab specific to the management of these template slides that form the bones of the presentation. You may well see lots of title slides or similar, which have embedded background images – if you know you don’t need those graphics or those layouts, just delete them.
This title slide in the Slide Master view had a graphical background which was 17Mb in size
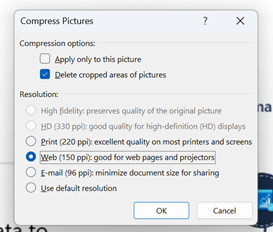
Selecting an image from one of the 70-odd slides in the deck, and choosing Compress Pictures from the Picture Format tab reduced it again to only 11MB, or 10% of the original file size – all for a few minutes’ effort.
†NB: the irony of sending a 2MB email to thousands of people, and sharing online and on LinkedIn, is not lost. |
629 – Edge Task, Man
|
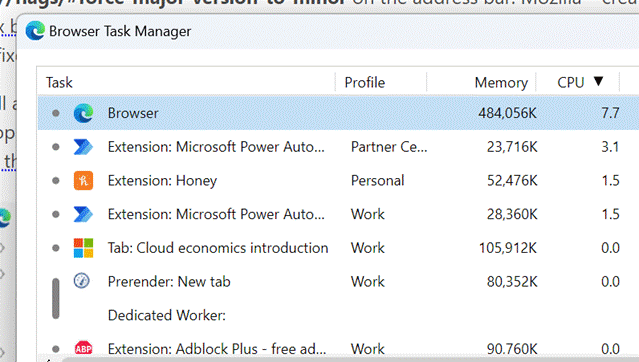
If you’re in Edge already, press SHIFT+ESC, or go to the “…” menu in the top right, choose More Tools > and find Browser task manager under there. Even though the main Windows Task Manager has been overhauled recently with extended support for Edge, the browser task man gives even more insight into what’s going on with the various tabs, extensions and supporting processes.
Right-click in the task list to add more columns to the display, like CPU Time to show longer-term vampire processes, or Profile, to display which of the potentially multiple browser profiles are hosting that tab or extension. If the browser is taking up a bit more CPU or memory than you think it should, it may be time to prune the installed extensions list somewhat (disabling certain extensions from lesser-user profiles or removing some altogether), or engage in a more protracted exercise to find out where the memory is being used.
Also, Edge is now 101, though there’s not much excitement for most users. |