|
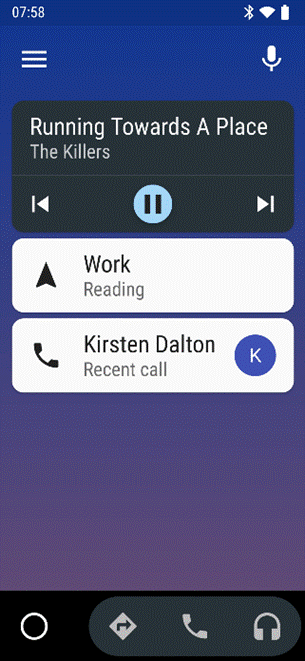
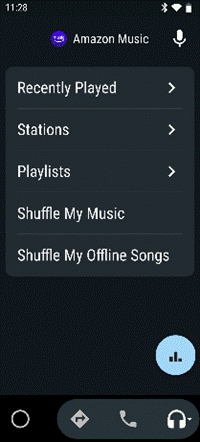
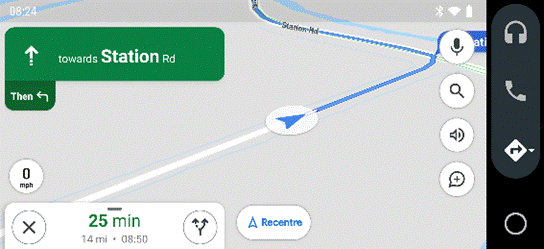
The main Android Auto app can either be run manually or set to start automatically when the phone connects to your car’s Bluetooth system. The app displays a simplified arms-reach or voice-driven UI, showing navigation, telephone and music apps, and the settings allow for a good amount of choice – Waze or Google Maps, Spotify or Amazon Music etc. Assuming you’re There are 120-odd Android Auto compatible apps, so even if you don’t see their UI on the main menu, you could respond (with voice) to incoming messages on WhatsApp, or choose to listen to podcasts with Stitcher as one of several interchangeable “music” apps. If your car does support Android Auto (check compatibility here) then it might take a bit of experimenting to understand how to connect it and how to get the car’s display to show the app outputs, though the results are largely the same as what you’d see if you just ran the host Android Auto app on your phone screen directly. You might be able to replace the satnav system in an older car with one which does support Android Auto – see here for some ideas – as aftermarket satnavs are increasingly simple, ditching a CD/DVD player and maybe not even having a radio tuner – perhaps all you need in your car stereo is a 7” screen to which your phone connects, and an amplifier. Some retro-fit satnav systems use Android as their own OS, and offer a whole host of Carlos Fandango features for little more than the cost of a maps update for an older in-car system. |
Month: October 2020
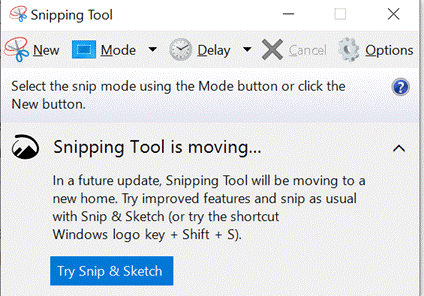
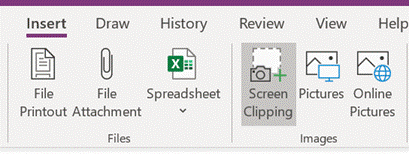
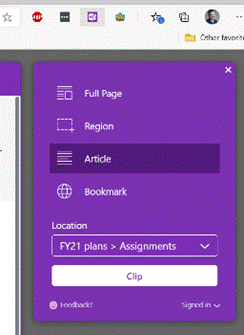
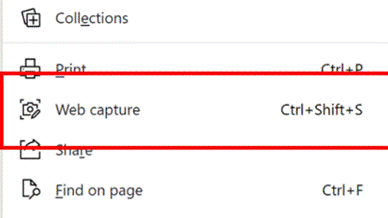
552 – snip snip, cap cap
|
There’s also the
Eventually, the new Edge will adopt some of the functionality that legacy Edge had when it comes to annotating web pages with ink, adding notes to pages etc – but the forthcoming web capture is a first step. Note – if you use Mouse Without Borders, it already has the CTRL+SHIFT+S keyboard combo in use, so you’ll need to change that… |
551 – Ticking away the moments
|
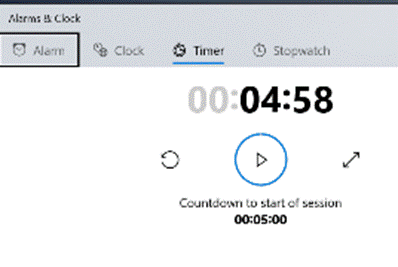
There’s a great little app built-in to Windows 10 called Alarms & Clock, which lets you set alarms on your PC, show a world map with multiple locations / time zones displayed, and also provides a neat countdown or count-up timer.
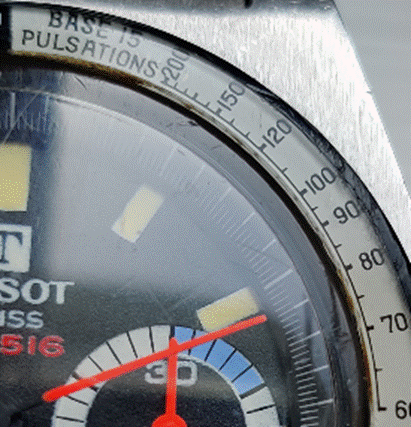
You can create multiple separately-controlled timers with different durations & names; so you could have an overall meeting countdown timer, and then a separate one for each participant, if you were acting as the time cop to keep everyone else in line. The Stopwatch is simply a fast-running counter of elapsed time, and by using the Those of us who still wear physical, mechanical wristwatches may be passingly familiar with a few features that have existed for decades to achieve the same kind of function, albeit more for individual rather than shared use. So called “diver” watches were popularised in the 1960s and 70s, as tough, waterproof and utilitarian. The most striking feature of any dive watch is generally the rotating numbered bezel which goes around the outside. The simple idea was that when you entered the water (knowing you might have 20 minutes of air), you would turn the bezel so the arrow / zero marker was set to where the minute hand was at that point – meaning a later glance at the watch will tell you how many minutes have passed since. Lots of other non-dive watches also have rotating bezels or indicators, and can be useful for things other than scuba – when the activity above started at 5 minutes to 10, the bezel was set, and it’s easy to see in a trice that was 11 or 12 minutes ago. Not sub-second accurate, but it’s a simple way to mark the passing of time. Many chronograph watches – which combine the function of a stopwatch and a regular timepiece – have a Tachymetre scale around the outside, yet most people these days will have no clue what it’s for. The basic function of the watch is that pusher buttons on the side will start and stop the movement of the chronograph hand which ticks round to indicate elapsed time. The deal with the TACHY scale is that if you know a distance – the length of a straight on a motor-racing track, for example – and you time something going over that distance, then you can quickly calculate its speed across the ground. In practice this is easier said than done, since the TACHY scale reads how many of the <distance> would be covered in an hour at this speed. If the measured distance was exactly 1km or 1mile then it’s an easy calculation – if it took 12 seconds to cover 1km, that would equate to 5km per minute or 300km/h. If the measured distance was a fraction – let’s say the length of the 12-second straight was 150m – then the calculation would be 300 x 150m per hour, or 45km/h. By the time you’ve done that in your head, the subject will be half a lap further on…
If you were cruising at 120km/h, and started the timer, then stopped it when it reached 120 on the scale… (after 30 seconds) – then you know you will have travelled 1km in that time. Yes, there probably are hundreds of times a month when you need to know exactly this. Pulsations
Watches with Pulsations bezels are sometimes nicknamed “Doctors’ watches” as the utility is to help count a patient’s pulse – the method being you start the chronograph, count 15 pulses and the corresponding number on the bezel would tell you what the pulse/minute rate is. Smart watches, eh, who needs them when you have space-age timing technology like this? |
550 – That’s not my name
|
If you have the kind of name that people habitually get wrong, there are things you can do to mitigate, like adopting a shorter and easier-to-pronounce and/or spell version. This tactic is often seen where people from cultures with long and complex names choose a “western” handle as well, just to make their own lives a bit easier. Or you could just put up with people getting your name wrong and don’t worry about it. An alternative trick is to provide people with your own pronunciation – that way, even if they forget, they can go back and check how you say your name. In the days of Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging, you could choose to record your own name, as well as calling in to set your voicemail greeting, manage your calendar and so on. Exchange UM made a great demo back in the day, but presumably didn’t get used enough as it has now gone away.
Tap on your own photo in the top left of the LinkedIn app, then choose View Profile – and the rest is fairly self-explanatory. You record your name, and after you’ve confirmed that you’re happy with the playback, save it and from now on, anyone who looks you up will see the speaker icon next to your profile name. Alternatively, YouTube has a variety of pronunciation tutorials. |
549 – Quick & easy screen recording
|
There are other more accessible and arguably easier ways for the modern PC user to capture the screen, though. You could start a Teams meeting with yourself (a handy way to check how you look and sound on video) by going to the Calendar node in Microsoft
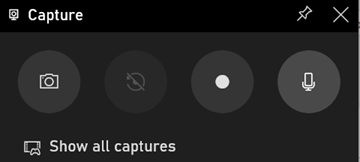
A simpler method might be to just go to the Stream portal – if you’re a subscriber to Microsoft 365 – and create a screen recording from there. If you’re not looking for anything too fancy, though, a quick & easy way to grab a recording of an application – not the whole screen, only the current app window – is to use the Xbox Game Bar that’s probably included in your Windows 10 install. Although the Game Bar is designed to be used for recording snippets of gameplay, it’s also a really neat way of capturing the video and audio of pretty much any other application; with a bit of practice, you could record your own instructions on how to carry out some task in an application, while showing just that app window, and it’ll be available to share in a few moments. Simply open the app you want to record, then press WindowsKey+G to bring up the overlay GameBar UI.
When you’re ready, press the round record button in the Capture dialog (or press WindowsKey+ALT+R), also making sure your mic isn’t muted if you want to record your voice. Once you’re live, you’ll see another
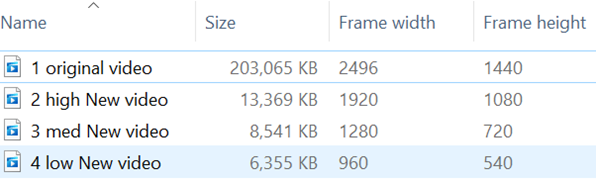
A 1m30s demo captured on a 4K display could easily be 200Mb in size; a quick solution is to use the built-in Video Editor in the Photos app.
|